Optimizing Water Usage with Smart Irrigation
Efficient water management has become a vital concern for both agricultural and urban landscapes. With growing awareness of environmental sustainability and fluctuating water availability, integrating smart irrigation technologies has emerged as a forward-thinking solution. Smart irrigation not only conserves precious water resources but also maximizes plant health and yields, reduces operational costs, and leverages data-driven insights for optimal scheduling. This page explores the key concepts, benefits, and considerations in optimizing water usage with smart irrigation systems, guiding you towards making informed, impactful choices for your landscape or farm.
The Importance of Water Conservation
Around the world, water scarcity affects billions, with agriculture consuming over 70% of fresh water supplies. Traditional irrigation methods often cause significant losses through evaporation and runoff, compounding the scarcity issue. By switching to smart solutions, users can directly contribute to global water conservation efforts, ensuring resources remain available for all sectors.
A typical smart irrigation system comprises soil moisture sensors, weather stations, automated valves, and programmable controllers. These components work in unison, monitoring moisture levels, detecting rainfall, measuring temperature, and adjusting irrigation schedules accordingly. The synergy between these elements ensures plants receive precise amounts of water, reducing both waste and associated costs.


Advantages of Smart Irrigation
Smart irrigation systems significantly reduce overwatering and minimize losses due to runoff and evaporation. By applying water only when and where it is needed—based on real-time measurements—these systems ensure maximum utilization per drop. This efficiency translates to water savings upwards of 30%, offering a meaningful contribution to both environmental protection and operational sustainability.

Soil moisture sensors accurately measure the volumetric water content at various soil depths. These readings inform the smart controller whether the soil is too dry, adequately moist, or overly saturated. Precise data eliminates speculative guesswork, ensuring the system triggers irrigation only when soil moisture levels fall below optimal thresholds.

Incorporating weather data—either via on-site weather stations or meteorological services—allows irrigation schedules to adapt to changing conditions such as rainfall, temperature, and evapotranspiration rates. If rain is expected or has just occurred, the system can postpone or reduce scheduled irrigation, preventing unnecessary watering and promoting efficient resource use.

IoT technology connects sensors, controllers, and user interfaces through wired or wireless networks. This real-time communication enables centralized control, remote diagnostics, and system updates. Rapid feedback loops allow users or automated algorithms to react swiftly to anomalies, leaks, or changing plant needs, ensuring constant optimization.

Assessing Farm Needs and Objectives
Successful implementation starts with evaluating the farm’s unique soil types, crop varieties, and local climate conditions. Understanding water needs at different growth stages enables the selection of compatible sensors and control strategies. Smart irrigation customization ensures that technology aligns with specific farm goals, whether maximizing yield, conserving water, or streamlining labor.
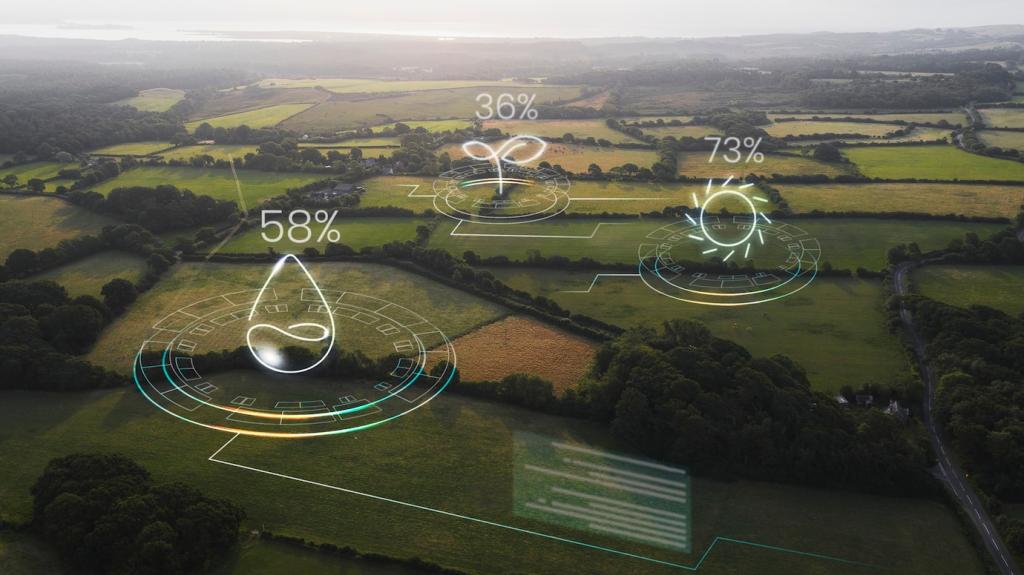
System Selection and Installation
Choosing the right smart irrigation system involves comparing sensor types, controller features, and compatibility with current infrastructure. Installation may require retrofitting existing systems or deploying entirely new networks of valves and sensors. Partnering with experienced vendors or consultants can smooth this process, minimizing disruptions and maximizing system performance from day one.

Monitoring and Continuous Optimization
Post-installation, farmers use the system’s analytics and reporting features to track water usage, crop health, and system efficiency over time. Continuous data analysis supports ongoing optimization—fine-tuning watering schedules, identifying unusual trends, and ensuring resources are always used to their fullest potential. This adaptive approach secures both immediate and lasting benefits.
Smart Irrigation for Residential and Commercial Landscapes
Uniform, healthy turf and flourishing plants take center stage in residential and commercial spaces. Smart irrigation systems ensure consistent watering, preventing patchy lawns or stunted plants often caused by manual or unscheduled watering. By providing optimal hydration, properties look their best throughout changing seasons, boosting enjoyment and real estate value.


Initial Costs and Budget Considerations
The upfront investment in smart irrigation—covering sensors, controllers, installation, and possible infrastructure upgrades—can be significant. However, strategic budgeting and access to water-saving incentives help offset costs over time. Moreover, long-term operational savings and increased yield often outweigh the initial expense, providing ongoing value.

Technical Integration and User Training
Transitioning from traditional to smart solutions may require new skills, not only in installation but also operation and data interpretation. Training users to navigate interfaces, interpret data, and troubleshoot minor issues is crucial to unlock the full potential of these systems. Many providers offer comprehensive support and educational resources to facilitate user adoption.
Future Trends in Smart Irrigation
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Emerging AI technologies are making it possible for irrigation systems to predict water needs days in advance using historical weather patterns, crop models, and machine learning algorithms. Such predictive analytics allow pre-emptive adjustments, further reducing waste and increasing responsiveness to unanticipated environmental changes.
Integration with Broader Smart Ecosystems
As part of the broader movement towards interconnected devices, smart irrigation is increasingly integrating with other smart-home or smart-farm systems. This enables comprehensive management of resources—such as syncing irrigation with fertilization schedules or integrating with building water conservation systems—creating unified, holistic control.
Sustainable Material and Energy Use
Future innovations focus on sustainability, with new systems incorporating energy-efficient components, solar-powered sensors, and recyclable materials. Enhancing both water and energy conservation ensures that smart irrigation continues to align with global sustainability goals, offering benefits for users and the environment alike.