Weather-Based Adjustments in Irrigation Systems
Weather-based adjustments in irrigation systems represent a significant advancement in smart agriculture and landscape management. By actively integrating current weather data and forecasts, these systems help optimize water usage, support healthier plant growth, and promote sustainability. Whether in residential gardens, commercial landscapes, or vast agricultural fields, weather-responsive irrigation technology adapts watering schedules and quantities based on real-time atmospheric conditions, resulting in efficient water delivery and reduced waste. This approach not only ensures better resource allocation but also helps in minimizing operational costs and improving environmental stewardship.
The Science Behind Meteorological Integration
The core science of weather-based irrigation revolves around integrating localized weather data with the specific water requirements of plants. By using sensors and weather stations or reliable data feeds, the system collects real-time information on parameters like precipitation, solar radiation, wind speed, and ambient humidity. Advanced algorithms then compute the exact irrigation needs, reflecting both the recent weather and the unique characteristics of the soil and vegetation present. This seamless combination of climate science and horticultural expertise not only conserves water but also improves yields and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for a variety of settings.
Types of Weather Data Sources Used
Efficient weather-based irrigation systems tap into diverse data sources to inform their decisions. Some rely on local weather stations installed directly on-site, which provide precise measurements tailored to the microclimate of the area. Others use regional and national meteorological services through network connections, granting access to broad forecasting models and historical trends. Additionally, many systems can integrate personal weather devices or even crowd-sourced weather platforms to further refine their data inputs. The greater the quality and specificity of the data, the more accurately an irrigation system can respond to natural changes, ensuring optimal results.
Benefits of Weather-Based Irrigation Adjustments
Water Conservation and Sustainability
Weather-based irrigation is a leading force in the pursuit of environmental sustainability. By automatically reducing or skipping watering cycles after rain or during periods of high humidity, these systems prevent unnecessary water usage. This proactive approach has been shown to save substantial volumes of water annually, which is critical in regions facing increasing scarcity. Moreover, efficient water management helps maintain aquifer levels and reduces runoff, lessening the environmental impact of irrigation and supporting the long-term health of local ecosystems.
Soil Moisture Sensors and Weather Stations
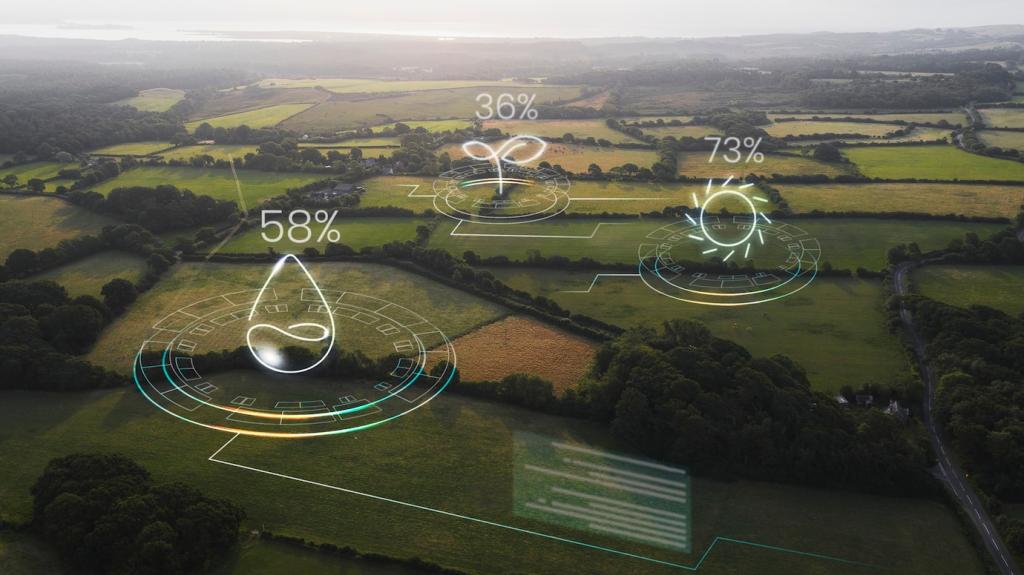
At the heart of adaptive irrigation are advanced sensors that measure soil moisture, temperature, and real-time weather conditions. These devices are strategically placed within landscapes or agricultural fields to capture granular, site-specific data. Soil moisture sensors, for example, detect the precise water content in the root zone, allowing for immediate, calibrated adjustments to watering schedules. Integrated weather stations track rainfall, wind, and sunlight, giving a comprehensive picture of environmental influences. When combined, these devices create a robust monitoring network that ensures every irrigation event is accurately targeted.
Cloud-Based Software and Analytics
The decision-making power of modern irrigation systems is amplified by cloud-based software platforms that aggregate and analyze all collected data. These platforms use predictive analytics and weather forecasting to tailor watering routines far beyond what traditional controllers offer. Advanced algorithms incorporate long-term weather patterns, real-time changes, and plant-specific needs, resulting in highly personalized irrigation strategies. Cloud connectivity allows for continuous updates and remote management, ensuring that the system remains responsive to both expected and unexpected changes in climate without manual input.
Smart Controllers and Connectivity
Smart irrigation controllers act as the command centers of weather-responsive systems. These programmable devices receive data from sensors, weather stations, and online services, then automatically regulate irrigation cycles in response. Many smart controllers are designed for compatibility with home automation systems and the Internet of Things (IoT), offering remote access via mobile apps or computer portals. Users can review performance metrics, alter program settings, and receive alerts, enabling proactive management even when away from the property. This level of connectivity ensures flexibility and rapid response to evolving weather conditions.